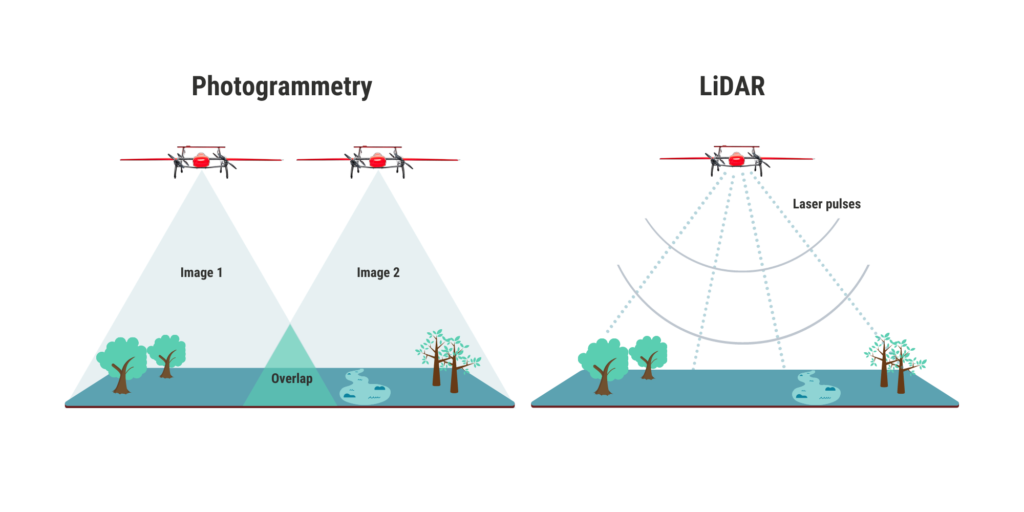
Over the past few years, we’ve seen an explosion in the use of drone technology across various industries. One of the most important applications of drone technology is in the field of mapping and surveying. In particular, drones equipped with LiDAR and photogrammetry sensors are revolutionizing how we collect data for various applications, from land surveying to infrastructure inspection.
LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) is a remote sensing technology that uses lasers to measure distances to objects. Essentially, a LiDAR sensor emits a laser pulse and measures the time it takes for that pulse to bounce back after hitting an object. The sensor can create a detailed 3D map of the environment by repeating this process thousands of times per second.
Photogrammetry, On the other hand, is the science of making measurements from photographs. In drone technology, photogrammetry sensors are cameras that capture high-resolution aerial images, which are then used to create 3D models of the terrain or objects in the environment. Combined, these two technologies can create highly accurate and detailed maps and models of the environment. Let’s take a closer look at each technology and how they work.
What is Lidar, and how it works?
LiDAR sensors come in various forms but all work on the same basic principle. The sensor emits a laser pulse that travels to the ground or other environmental objects. When the pulse hits an object, it reflects back to the sensor, which measures the time it took for the pulse to return. By knowing the speed of light, the sensor can calculate the distance between the sensor and the object.
The LiDAR sensor typically rotates 360 degrees as it emits pulses, creating a point cloud of data that can be used to create a 3D model of the environment. This data can be used for various applications, from creating topographical maps to detecting changes in terrain or vegetation over time.
LiDAR sensors are handy when accuracy is critical, such as in land surveying, engineering, and construction. They can quickly and accurately measure distances, angles, and heights, which makes them valuable tools for these industries.
Advantages and limitations of Lidar
Lidar is a powerful technology that offers many advantages for land surveying with drones. Here are some of the key advantages and limitations of Lidar:
Advantages:
- High Accuracy: LiDAR technology provides highly accurate 3D measurements of the environment. The accuracy of LiDAR data can be as high as a few centimeters, depending on the sensor and the data processing methods used.
- Rapid Data Acquisition: LiDAR systems can quickly capture large amounts of data over a wide area. This means LiDAR can rapidly survey large land areas, such as forests, coastlines, and urban regions.
- High Data Density: LiDAR data is dense, meaning it contains many data points. This makes it possible to generate detailed 3D models of the environment, including features such as buildings, trees, and terrain.
- Non-Invasive: LiDAR technology is non-invasive, meaning it does not require physical contact with the surveyed environment. This makes it possible to survey areas that would be difficult or impossible to survey using ground-based methods.
- Ability to Penetrate Vegetation: LiDAR signals can penetrate vegetation to some extent, making it possible to survey forested areas and other environments with dense vegetation.
- Can Be Used at Night: LiDAR can be used at night or in low-light conditions, as it uses its own light source to capture data.
- Can Be Combined with Other Technologies: LiDAR data can be combined with data from other sensors, such as cameras, to create highly detailed and accurate 3D models of the environment.
Limitations:
- Limited Range: LiDAR technology is limited by its range. The maximum range of most LiDAR sensors is around 100 meters, although some systems can reach up to 300 meters. Beyond this range, LiDAR becomes less accurate and reliable.
- Weather Conditions: LiDAR technology can be affected by adverse weather conditions, such as heavy rain or fog. These conditions can cause the LiDAR signal to bounce off particles in the air, making it difficult to obtain accurate readings.
- Cost: LiDAR sensors are expensive, making them prohibitive for some applications. The cost of LiDAR systems can range from a few thousand to tens of thousands of dollars.
- Limited Penetration: LiDAR signals cannot penetrate some materials, such as thick vegetation or water. This can make it difficult to measure objects or terrain behind these obstacles accurately.
- Limited Spatial Resolution: LiDAR data is limited by the spatial resolution of the sensor. This means that small or detailed features may not be accurately represented in the LiDAR data, leading to potential errors or inaccuracies in the resulting point cloud.
What is Photogrammetry, and how it works?
Photogrammetry is the process of creating 3D models from photographs. In drone technology, photogrammetry sensors are typically high-resolution cameras that capture images from multiple angles as the drone flies over the region of interest.
These images are then processed using specialized software to stitch them together to create a 3D model of the terrain or object. This model can be used for various applications, from creating maps and models of buildings to monitoring changes in vegetation over time.
One of the key advantages of Photogrammetry is that it allows for highly detailed and accurate models to be created. The high-resolution images captured by the drone can be used to create models with millimeter-level accuracy, which makes them valuable tools for industries such as architecture and engineering.
Advantages and limitations of Photogrammetry
Photogrammetry is a versatile technology that offers many advantages for land surveying with drones. Here are some of the key advantages and limitations of Photogrammetry:
Advantages:
- Cost-Effective: Photogrammetry is generally more cost-effective than LiDAR technology. It requires less specialized equipment and can be conducted with standard cameras and drones.
- Cost-Effective: Photogrammetry is generally more cost-effective than LiDAR technology. It requires less specialized equipment and can be conducted with standard cameras and drones.
- Large Area Coverage: Photogrammetry can quickly and efficiently cover large land areas. This makes it an ideal technology for large-scale mapping projects.
- Non-Invasive: Similar to LiDAR, Photogrammetry is non-invasive and does not require physical contact with the environment being surveyed.
- Versatility: Photogrammetry can be used in a variety of applications, such as mapping terrain, monitoring construction progress, and creating 3D models of buildings and other structures.
- Integration with Other Technologies: Photogrammetry data can be easily integrated with other technologies, such as LiDAR and GPS, to enhance its accuracy and generate highly detailed and accurate 3D models.
- Integration with Other Technologies: Photogrammetry data can be easily integrated with other technologies, such as LiDAR and GPS, to enhance its accuracy and generate highly detailed and accurate 3D models.
Limitations:
- Weather Conditions: While Photogrammetry is not affected by adverse weather conditions like LiDAR, it is affected by strong winds, which can cause the drone to shake and affect the quality of the images. It is also affected by low-light conditions and cloud cover, which can impact image quality and reduce the data’s accuracy.
- Requires Good Image Quality: Photogrammetry requires high-quality images to generate accurate 3D models. This means the camera should have a high resolution and good optics, and the photos should be free from motion blur and other distortions.
- Complex Data Processing: Photogrammetry data requires complex processing to generate accurate 3D models. This processing involves stitching together multiple images, identifying and matching features between images, and developing a 3D model from the resulting data. This process can be time-consuming and requires specialized software and expertise.
- Limited Penetration of Vegetation: Photogrammetry is limited in penetrating vegetation. This means that in areas with dense vegetation, the accuracy of the data may be reduced.
- Limited Depth Perception: Photogrammetry technology relies on the parallax effect, which is the apparent shift in the position of objects when viewed from different angles. This means that Photogrammetry may have limited depth perception compared to LiDAR technology.
- Limited Accuracy in Low-Contrast Environments: Photogrammetry may struggle to capture data accurately in low-contrast environments such as featureless landscapes or snowy terrain.
Differences between Lidar and Photogrammetry
While Lidar and Photogrammetry are used to create 3D models of objects and terrain, the two technologies have some significant differences.
One of the main differences between Lidar and Photogrammetry is the data type they produce. Lidar sensors make highly accurate 3D point cloud data, which provides precise measurements of the distance between the sensor and the target. Photogrammetry, on the other hand, produces 3D models based on image data, which may be less accurate than lidar data.
Another difference between Lidar and Photogrammetry is the cost. Lidar sensors are typically more expensive than cameras, making them less accessible for small-scale projects. Photogrammetry, on the other hand, can be performed with a standard drone-mounted camera, making it more affordable for smaller projects.
Combining LiDAR and Photogrammetry
While LiDAR and Photogrammetry are powerful technologies, combining them can create even more detailed and accurate maps and models.
A drone equipped with both LiDAR and photogrammetry sensors could capture data about an environment, and the data from the two sensors could be combined to create a more detailed 3D model than either sensor could make on its own.
There are several advantages to combining LiDAR and Photogrammetry:
- LiDAR provides accurate distance measurements that can be used to improve the accuracy of photogrammetry data.
- LiDAR can capture data about environments that may not be visible in photographs, such as the bridge’s underside or the building’s interior.
- Combining LiDAR and Photogrammetry can provide a complete picture of an environment, which can be helpful in various applications, from construction and engineering to environmental monitoring and conservation.
One example of the use of combined LiDAR and Photogrammetry is in archaeology. LiDAR data can be used to create a detailed DSM of an archaeological site, which can then be used to refine photogrammetry data to create an accurate 3D model. This can be useful in identifying features that may not be visible on the surface, such as buried structures or changes in the site’s topography.
Another example is in the field of forestry. LiDAR data can generate accurate measurements of tree height and density, while photogrammetry data can create detailed 3D models of the forest canopy. By combining these two data sets, researchers can gain a complete understanding of the forest ecosystem, including the distribution of species and the impact of environmental factors such as climate change and forest management practices.
Factors to consider when choosing between Lidar and Photogrammetry.
When choosing between Lidar and Photogrammetry for your drone land surveying project, there are several factors to consider.
One crucial factor is the type of data needed for the project. Lidar may be the better choice if the project requires highly accurate elevation data. On the other hand, if the project requires detailed imagery, Photogrammetry may be the better choice.
Another factor to consider is the cost of the technology. Lidar sensors are more expensive than cameras, making Lidar a less cost-effective option for some projects. However, Lidar is often faster and more efficient at capturing data, which can offset the higher cost.
The type of project being undertaken is also an important factor. Different types of projects may require different types of data, and one technology may be better suited depending on the project’s specific requirements.
Finally, it is important to consider the expertise of the surveying team. Both Lidar and Photogrammetry require specialized knowledge and equipment to use effectively. If your team has more experience with one technology than the other, that may be the better choice for your project.
Cost comparison between Lidar and Photogrammetry
While Lidar and Photogrammetry have advantages and limitations, the cost is often a deciding factor when choosing between the two.
Lidar sensors can cost tens of thousands of dollars, while drones equipped with cameras can be purchased for a few thousand dollars. Additionally, the cost of acquiring and processing lidar data can be much higher than that of acquiring and processing photogrammetry data.
However, it is important to consider the project’s specific needs when comparing costs. For example, if the project requires highly accurate elevation data, the higher cost of Lidar may be worth it. On the other hand, if the project primarily requires detailed imagery, Photogrammetry may be the more cost-effective option.
To know more about reducing the cost of the land survey project read “11 Ways To Reduce Cost Of A Land Survey On Your Next Project”.
CONCLUSION
Lidar and photogrammetry technology have revolutionized the drone industry, opening up various applications in land surveying, agriculture, construction, and environmental monitoring. While Lidar provides highly accurate 3D point cloud data, Photogrammetry provides high-resolution image data that can be used to create detailed 3D models. Both technologies have advantages and disadvantages, but they have enabled drone operators to collect data and create 3D models that would be difficult or impossible to obtain using traditional surveying methods. As drone technology advances, Lidar & Photogrammetry will likely play an increasingly significant role in the industry, providing new insights and opportunities for businesses and organizations.